Before you continue, review System requirements for Microsoft Defender Application Guard to review the hardware and software installation requirements for Microsoft Defender Application Guard.
Note
Microsoft Defender Application Guard is not supported on VMs and VDI environment. For testing and automation on non-production machines, you may enable WDAG on a VM by enabling Hyper-V nested virtualization on the host.
Prepare for Microsoft Defender Application Guard
Before you can install and use Microsoft Defender Application Guard, you must determine which way you intend to use it in your enterprise. You can use Application Guard in either Standalone or Enterprise-managed mode.
Standalone mode
Employees can use hardware-isolated browsing sessions without any administrator or management policy configuration. In this mode, you must install Application Guard and then the employee must manually start Microsoft Edge in Application Guard while browsing untrusted sites. For an example of how this works, see the Application Guard in standalone mode testing scenario.
Standalone mode is applicable for:
- Windows 10 Enterprise edition, version 1709 and later
- Windows 10 Pro edition, version 1803 and later
- Windows 11 and later
Enterprise-managed mode
You and your security department can define your corporate boundaries by explicitly adding trusted domains and by customizing the Application Guard experience to meet and enforce your needs on employee devices. Enterprise-managed mode also automatically redirects any browser requests to add non-enterprise domain(s) in the container.
Enterprise-managed mode is applicable for:
- Windows 10 Enterprise edition, version 1709 and later
- Windows 11 and later
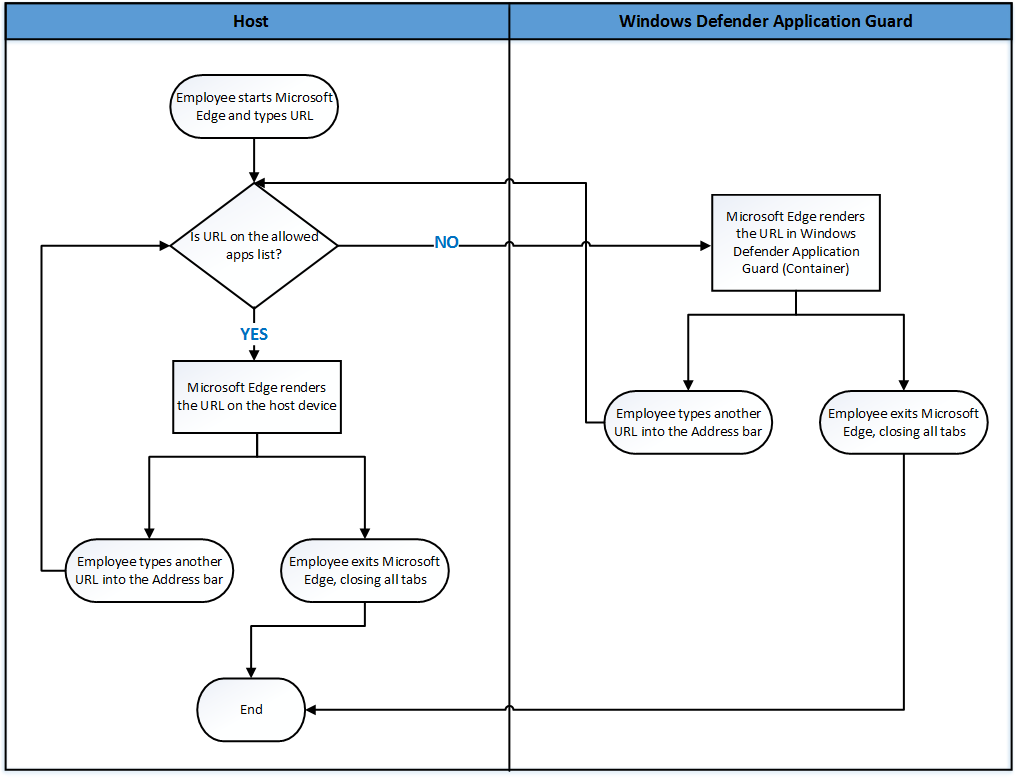
The following diagram shows the flow between the host PC and the isolated container.
Install Application Guard
Application Guard functionality is turned off by default. However, you can quickly install it on your employee’s devices through the Control Panel, PowerShell, or your mobile device management (MDM) solution.
Install from Control Panel
- Open the Control Panel, select Programs, and then select Turn Windows features on or off.
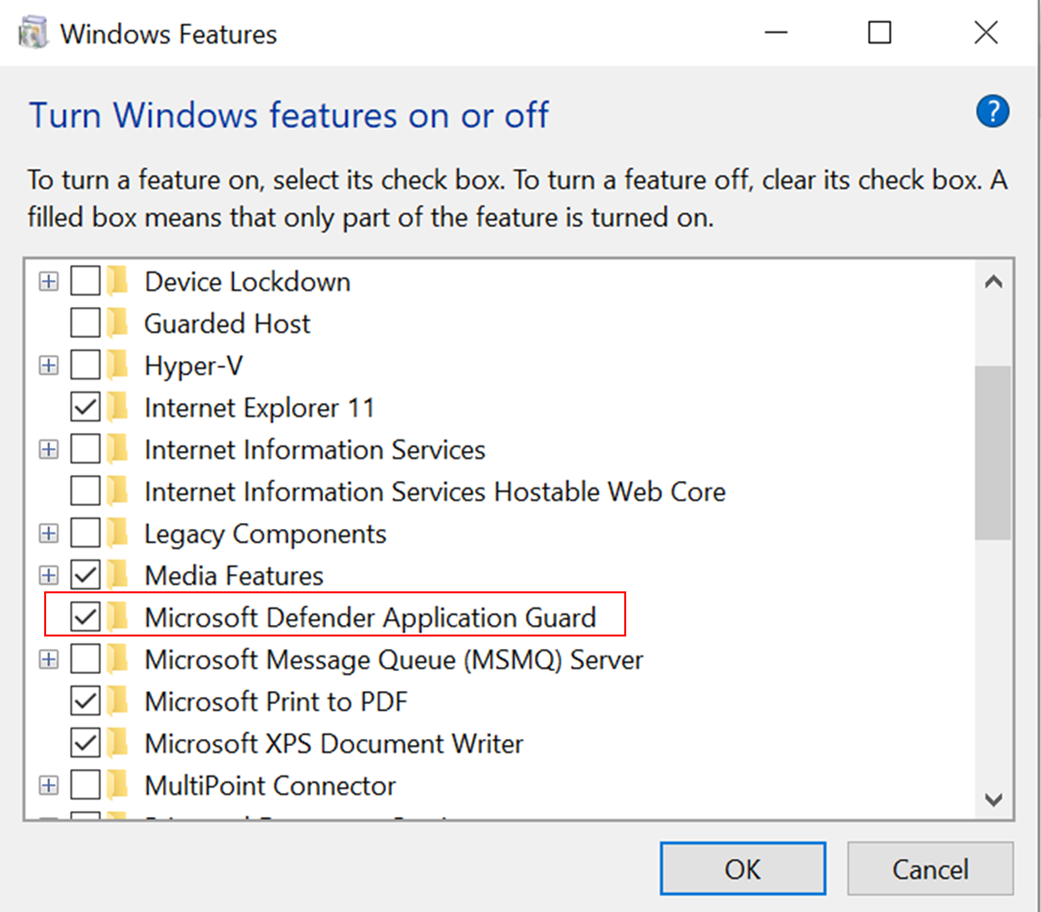
- Select the check box next to Microsoft Defender Application Guard and then select OK to install Application Guard and its underlying dependencies.
Install from PowerShell
Note
Ensure your devices have met all system requirements prior to this step. PowerShell will install the feature without checking system requirements. If your devices don’t meet the system requirements, Application Guard may not work. This step is recommended for enterprise managed scenarios only.
- Select the Search icon in the Windows taskbar and type PowerShell.
- Right-click Windows PowerShell, and then select Run as administrator to open Windows PowerShell with administrator credentials.
- Type the following command:PowerShellCopy
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName Windows-Defender-ApplicationGuard - Restart the device to install Application Guard and its underlying dependencies.
Install from Intune
Important
Make sure your organization’s devices meet requirements and are enrolled in Intune.
- Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
- Select Endpoint security > Attack surface reduction > Create Policy, and do the following:
- In the Platform list, select Windows 10 and later.
- In the Profile type, select App and browser isolation.
- Select Create.
- In the Basics tab, specify the Name and Description for the policy. Select Next.
- In the Configuration settings tab, configure the Application Guard settings, as desired. Select Next.
- In the Scope tags tab, if your organization is using scope tags, choose + Select scope tags, and then select the tags you want to use. Select Next.To learn more about scope tags, see Use role-based access control (RBAC) and scope tags for distributed IT.
- In the Assignments page, select the users or groups that will receive the policy. Select Next.To learn more about assigning policies, see Assign policies in Microsoft Intune.
- Review your settings, and then select Create.
After the policy is created, any devices to which the policy should apply will have Microsoft Defender Application Guard enabled. Users might have to restart their devices in order for protection to be in place.
Ref: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/threat-protection/microsoft-defender-application-guard/install-md-app-guard